As someone who has dealt with bathroom renovations and repairs, I’ve come to appreciate the importance of understanding the anatomy of a bathroom faucet. Knowing the various components that make up a faucet makes it easier to diagnose issues, make repairs, or even choose a new faucet that suits your needs. In this article, I’ll provide a straightforward guide to the anatomy of a bathroom faucet.
Spout: The spout is the part of the faucet where the water flows out. It extends over the sink and comes in different shapes and lengths, depending on the style of the faucet. Some faucets have a stationary spout, while others may have a swivel feature that allows you to direct the water flow.
Handles: Faucets typically have one or two handles that control the water temperature and flow. A single-handle faucet uses a lever-style handle to adjust hot and cold water. In a double-handle faucet, separate handles are used for hot and cold water. Handles can be operated by turning, lifting, or pulling, depending on the design.
Cartridge: The cartridge is a crucial component that regulates the water flow and controls the mixing hot and cold water. It is located inside the handle and consists of a valve that opens or closes to control the water flow. Cartridges can be made of ceramic, brass, or plastic and may need to be replaced if there are leaks or other issues.
Aerators: Aerators are small devices attached to the tip of the spout. They mix air with the water, creating a smooth and consistent flow while reducing water usage. Aerators also help prevent splashing and can be easily removed for cleaning or replacement.
Valve: The valve is responsible for controlling the water flow within the faucet. It is typically located inside the body of the faucet and is operated by the handles or a control mechanism. Valves can come in different types, such as compression, ball, cartridge, or ceramic disc valves, each with its water flow regulation method.
Supply Lines: The supply lines are the pipes that connect the faucet to the water supply valves under the sink. They deliver hot and cold water to the faucet, allowing you to control the water temperature and flow. Supply lines are usually made of flexible materials like braided stainless steel or plastic.
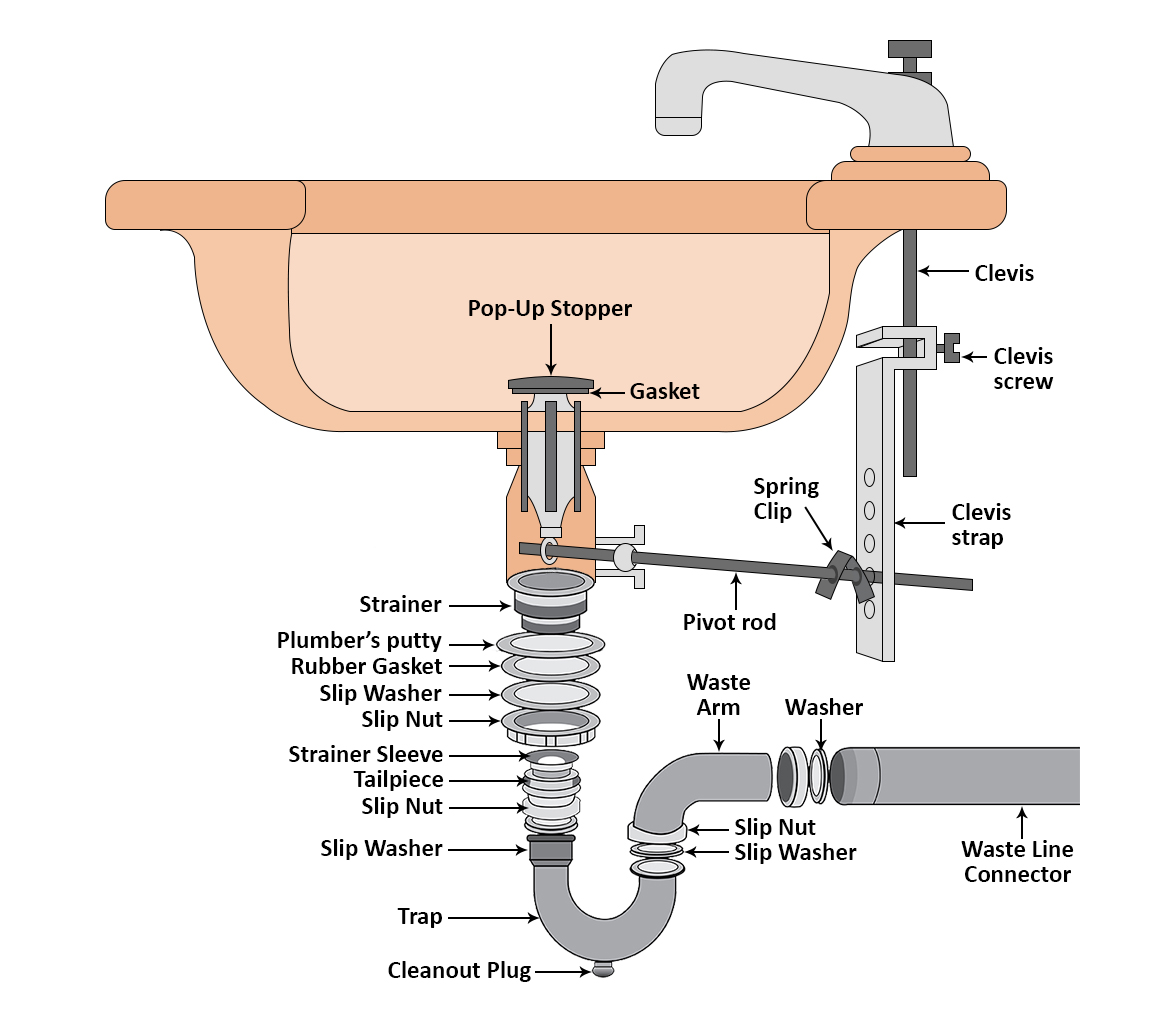
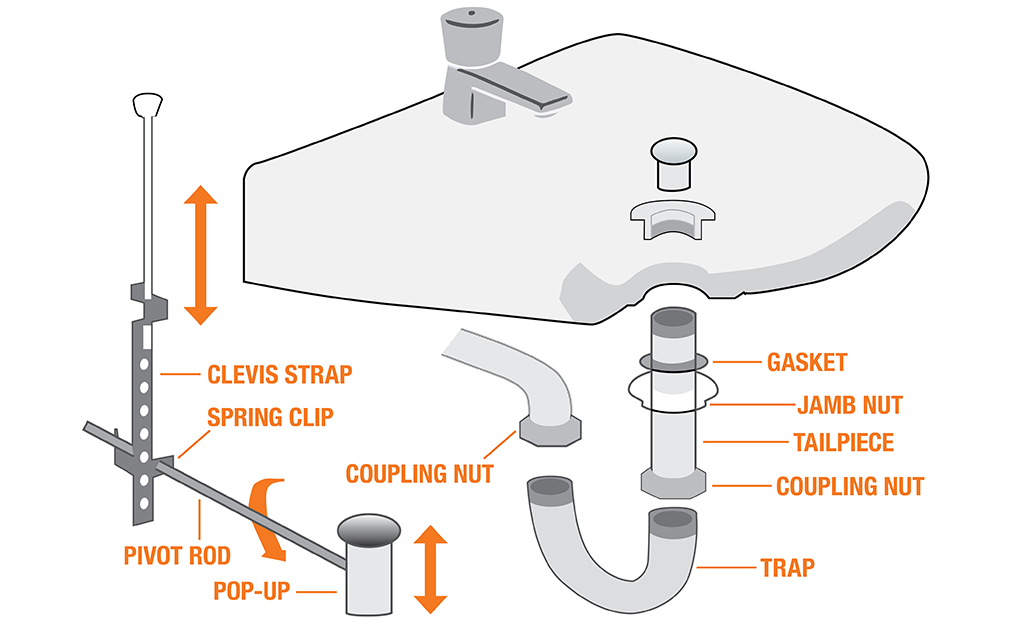
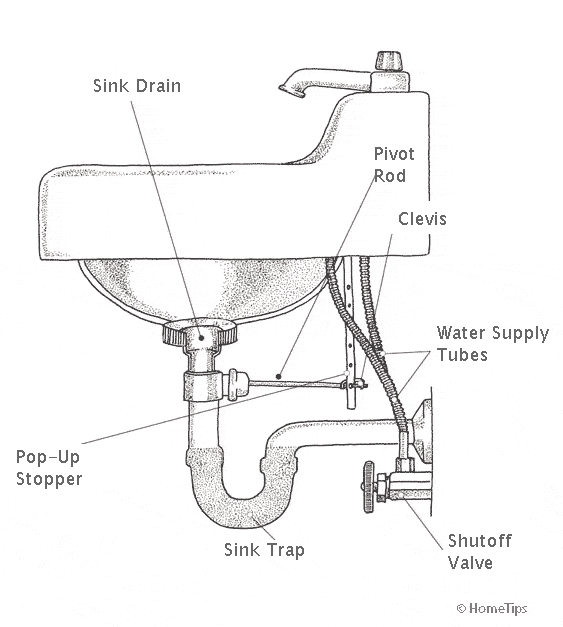
Drain Assembly: While not directly a part of the faucet, the drain assembly is essential to the bathroom sink system. It includes the drain stopper or plug, the lift rod, and the drain pipe. These components work together to control the draining of water from the sink basin.
Understanding the different parts of a bathroom faucet empowers you to troubleshoot issues and make informed decisions when it comes to repairs or replacements. Whether tackling a leak, upgrading your faucet, or simply maintaining its performance, having a grasp of the faucet’s anatomy is a valuable asset for any homeowner.
Anatomy Of A Bathroom Faucet
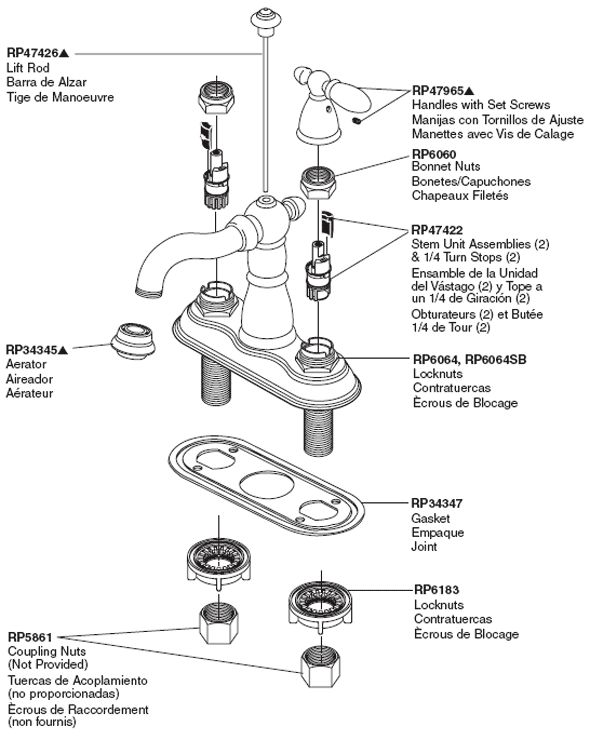
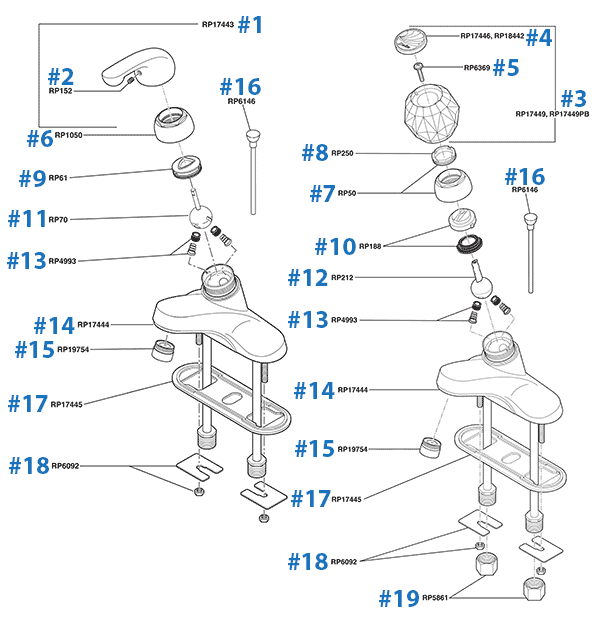
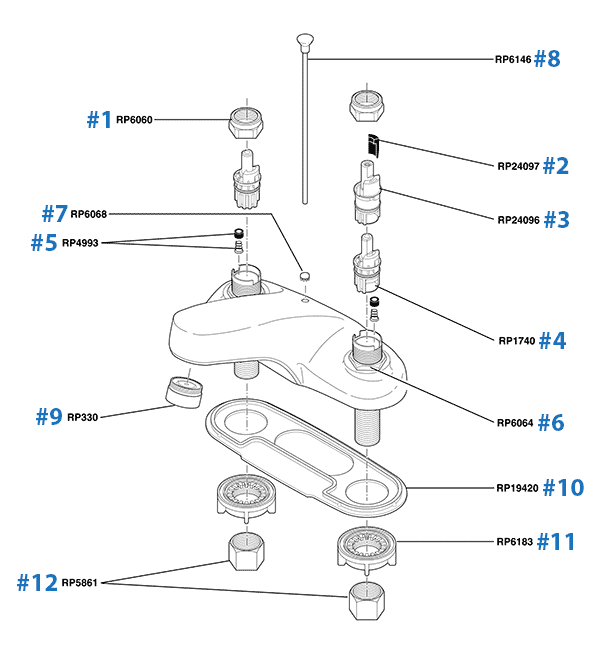
Repair Parts for One and Two Handle Delta Bathroom Faucets
Bathroom Sink Plumbing
Repair Parts for One and Two Handle Delta Bathroom Faucets
Bathroom Sink Plumbing
How to Replace a Bathroom Faucet – This Old House
How to Install a Bathroom Sink Wayfair
Faucet Parts – The Home Depot
Bob Oates Plumbing on Twitter: “The anatomy of a sink. #Plumbing
How Do Faucets Work? (5 Different Types Explained!)
Uživatel Núria de Andrés na Twitteru: u201eBathroom Sink Parts
Faucet Parts – The Home Depot
How to Connect a Bathroom Sink Drain?
Related Posts:
- Menards Bathroom Faucets Chrome
- Miseno Bathroom Faucets
- How To Repair A Delta Two Handle Bathroom Faucet
- Bathroom Faucet Replacement Parts
- Moen Kingsley Bathroom Faucet
- Dryden Widespread Bathroom Faucet
- Connect Hose To Bathroom Faucet
- Moen Vs Delta Bathroom Faucets
- Pfister Ladera Bathroom Faucet
- Premier Bathroom Faucet

:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/19497757/faucet_illo.jpg)